Haunted by Waters
...the north and the Midwest will undergo an economic and population resurgence in the coming decades because of water. Single states with thousands of lakes can support businesses and families far more affordably than the desert Southwest.

We were young when we lived near the Rio Grande and sometimes on Fridays the boss took us out on his boat and a few of my colleagues were pulled on water skis. I mostly remember the children sitting on their haunches in the canebrakes and how they stared at us with dark confused eyes. I assumed they wondered about the strange world along the north bank and the people who had boats for toys and never worried about food or where they might sleep at night.
There were times we slept on the beach down where the big river meets the Gulf, and we drank cold beer and watched the gulls as they whirled around the shrimp boats. In the mornings before the sun was above the coastline, I ran along the levees that were filled with water to grow the orange and grapefruit trees and I saw the open gates that let the water into the aloe and vegetable fields. When it got too hot, I jumped off the levee into the canal and swam with the slow current, kicking with my running shoes.
Our first season in the sub-tropics of Texas a moderate hurricane spun up from the Bay of Campeche and flooded the valley with torrential rains for a few days. Roads were closed and in the big colonias the farmworkers were washed out of their houses and into the mud. In the summer, giant thunderstorms rose across the fields and the humid air felt too thick to breathe. Wind across the Gulf and up through the palm rows felt like a hot, fuzzy cloth on the skin.
There seemed to be water everywhere in the Rio Grande Valley, though I never saw a lake, which was more than confusing. There were resacas, small bodies of water like ponds that were oxbow lakes cut off from the river, but the nearest big lake was northwest up the border toward Laredo. Falcon Lake, however, was a reservoir that had been backed up behind a dam on the Rio Grande. During a long drought, I took a small motorboat out on the water there with a camera crew, and we floated through an old stone church that had been disappeared beneath the water off the shore of the town of Zapata.
My childhood had been spent surrounded by water. The Great Lakes were in every direction, except to the south, and there were recreational lakes in such abundance it often felt like there was one at the end of every street. My parents found jobs in a factory town when they came up from the South, but we were of very modest means and I did not see a Great Lake until I was 18, even though we lived only an hour from Huron. In school, I had stared at pictures of the freighters filled with iron ore that moved across the big waters and I had always wanted to see one of the leviathans as a boy. Instead, on those rare days when my parents had time and the slightest amount of residual energy, we might go to a nearby lake for relaxation. There were untold thousands of crystalline blue bodies of water, too many, in fact, for each to have a name.
I always assumed an abundance of water was available in the world, but as I moved my journalistic and peripatetic soul around Texas, I came to the crushing comprehension that water was more precious than oil. All the water that will ever be is the water that exists presently, and it is readily apparent Texas was a bit shortchanged by geology. During a 250-million-year period of the Paleozoic Era, 600-350 million years ago, Texas was awash in vast inland seas to the West of the Llano uplift, which is in the central part of the state. In 2021, there are only rivers that have been dammed to create reservoirs. Underground aquifers also provide water, but they are increasingly mismanaged and endangered.
The rivers I knew in my youth ran mostly wild and free and we rented or found old and dented aluminum canoes to ride those rivers on weekends from college. The White River, Pine, and Au Sable moved placidly and sometimes rapidly through birch and white pine forests, running past cabins and under country roads toward the big lakes. There was no need for dams with such an endless surplus of water, but every river in Texas seems to be stopped to provide water for communities and agriculture, and even offer flood control. I believe the state’s only remaining unimpeded rivers are the Devil’s and the much fought over Pecos, which is a timid stream coming down from New Mexico and across the Chihuahua Desert to the Rio Grande at Lake Amistad.
Even barricaded, though, Texas rivers can be deadly. The weather seems too often to be about extremes, almost bombast in this state. Biblical floods and epic droughts torture the landscape of Texas. Rainfall in extreme amounts has its power amplified by the characteristics of runoff. The ground west of the Balcones Escarpment, a geographic break in the land that runs from near San Antonio to Fort Worth, is mostly rock and does not adequately absorb moisture. Water races downward to arroyos that feed rivers and can generate giant waves racing down riverbeds.
I saw the consequences of hard rain on rock many years ago when floods moved through the watersheds of the Pedernales and Guadalupe Rivers. In 1983, young campers in Pedernales Falls State Park were swept away by a flood in the night, and five died. Warning horns were later installed on the riverbank to let people know downstream of approaching high water. The sedate Blanco River, which lowers itself out of the Texas Hill Country through tall stands of cypress trees and long limestone cliffs, rose 28 feet in 90 minutes in late May of 2015, and killed more than a dozen people, many sleeping in riverside vacation homes. The water crested at 40 feet above flood stage when 13 inches of rain had fallen in the upstream watershed.
The most tragic flash flood incident in recent memory, however, was in 1987 on the Guadalupe River near Comfort. A group of campers from a Dallas church were cut off from safety as the water rose. An attempt to cross a low concrete bridge in their bus turned deadly when the engine stalled. A young student-athlete named John Bankston Jr. rescued several of the smaller children by carrying them out on his back as the water kept climbing up the side of the bus. He was unable to save himself, however, and was taken away by the rushing water and died with nine of his friends that morning. His body was the only one not recovered.
I will never forget flying up and down the river in a helicopter with John Bankston Sr., convinced he was going to find his son alive, clinging to a tree, even five days later. Thirty-four years after the tragedy, the river has not given up all its dead and no trace of Bankston Jr. has ever been found.
Texas is, however, as deadly dry as it is wet. Historic droughts are becoming dangerously recurrent as the state’s population dramatically increases with in-migration from the West and North. Newcomers, accustomed to green lawns and irrigation systems for their yards, move up into the arid Hill Country and plant thirsty St. Augustine grass. Every new home is another straw sipping from the reservoirs, which, increasingly in the added heat of climate change, have turned into what a Texas drought expert refers to as “giant evaporation ponds.” In fact, evaporation rates of surface water in the Hill Country are approximately 57 inches per year.
A significant portion of water in Texas that is not consumed by lawn sprinklers, washing cars, or getting flushed down toilets, is evaporating from the surface of lakes. The city of Las Vegas, Nevada is trying to stop the waste of water on what it describes as “ornamental grass.” The definition does not include front lawns but would put an end to watering medians on roadways or grass berms between sidewalks and pavement. The Southern Nevada Water Authority says there are eight square miles of “non-functional turf” in the Vegas area and eliminating its irrigation will reduce water consumption by about 15 gallons per person, per day.
A similar policy would help Texas conserve water.
“The easiest and quickest thing you can do—after patching up leaks—is restrict ornamental lawns,” said Alyssa Burgin of the Texas Drought Project. “Our major cities are growing so fast—we have to restrict it NOW. Folks who come here from elsewhere, where there is water, are just going to have to adapt. Heck, people who move to San Antonio from Bell County, where HOA/deed restrictions against xeriscaped lawns are enforced even when state law now states otherwise—are just going to have to adapt, because when the aquifer goes down, you’re going to go brown. Period.”
Storing water below ground, protected from the summer heat in the Southwest, is also an effective strategy. The practice of aquifer storage and recovery is being used in San Antonio and Kerrville with considerable success. A billion gallons of fresh drinking water are stored in the Kerrville aquifer facility, which was the first deployed in Texas and only the third in the entire country.
The frenzy of dam building that began after the historic drought of the 1950s has not solved our water problem in Texas. There are more than 200 dams in the state but every year they seem to approach dangerously low levels of storage. Because of our southern geographic coordinates on the map, Texas did not experience the southward movement of the ancient ice masses and, consequently, there are no glaciated bodies of water in the state, just small freshwater ponds, and little lakes, which has prompted a dependence on reservoirs.
The other problem, which legislators refuse to confront, is Texas does not have a uniform statewide water usage policy. We rely on outdated frontier water laws that preserve claims of “first in time, first in right,” and the “right of capture.” The latter expression, almost self-explanatory, means you own whatever water is under your land if you have a pump to bring it up. The right of capture empowers you to pump dry an aquifer you share with a neighbor simply because you might have the resources to buy a pump, and she does not. Obviously, there is no argument to be made that this approach serves a common good in the parched American West.
The Ogallala Aquifer, as an example, is being pumped dry by farmers pulling up water from beneath their land to irrigate crops that would not otherwise survive. Ogallala, a vast inland and underground sea that stretches from South Dakota to the South Plains of Texas, might take millennia to recharge if it is drawn down toward dry. Without the Ogallala, the cotton and wheat fields stretched across the Texas Panhandle and down through the Cap Rock will disappear, if the rains don’t come.
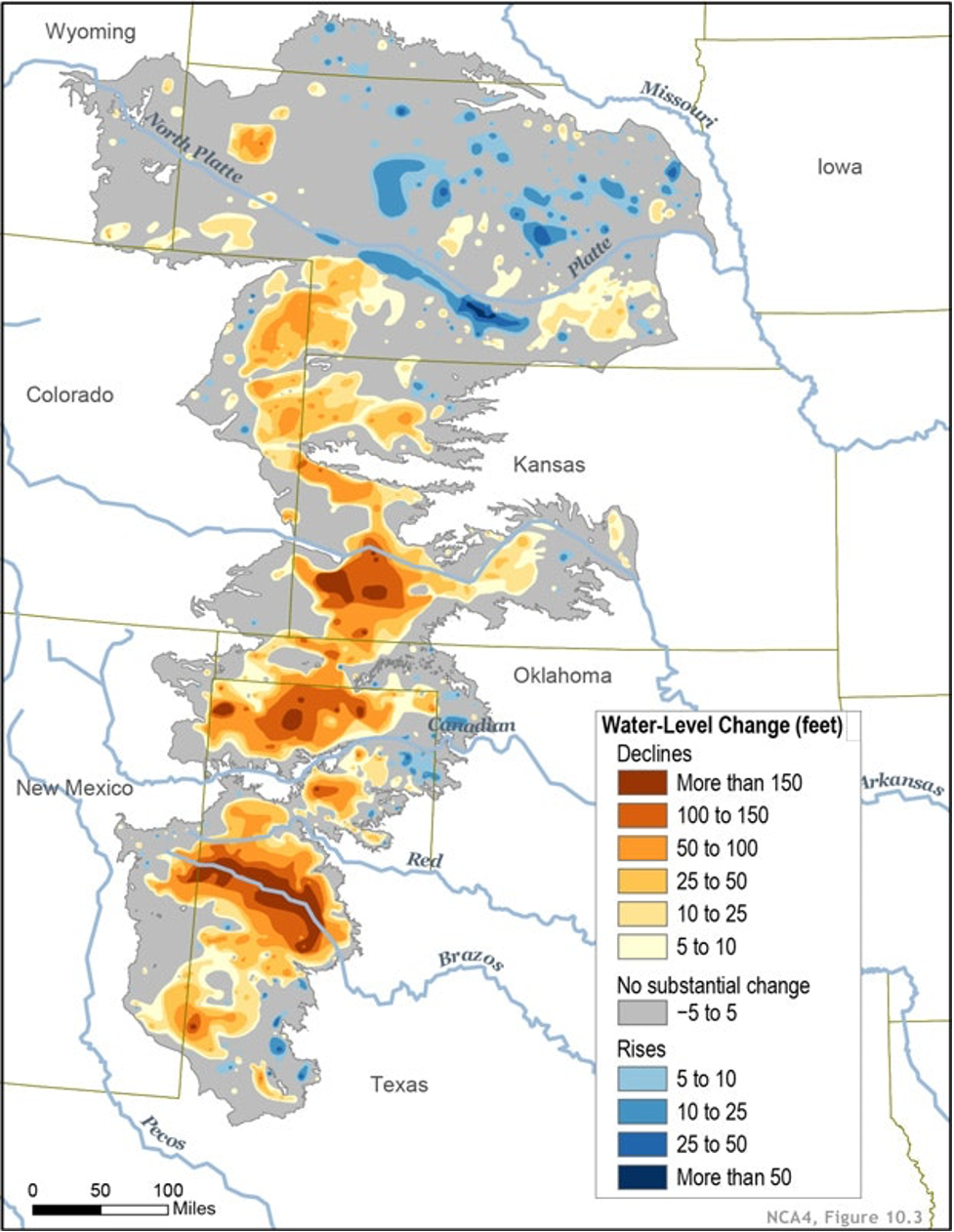
I remember an exploratory trip through Western Nebraska that led to reporting on an irrigation project in the sandhills. Center pivot rigs were crawling up and down the low hills, spitting out water and nitrate fertilizer. The project seemed absurd, but a western beef producer had decided to vertically integrate its business and grow its own corn for cattle feed, and the sandhills were close to operations, easily fertilized, and abundant water in the form of the Ogallala was just below the surface. The operation, even through my youthful eyes, seemed astonishingly stupid. The nitrates leached into the groundwater, polluted the aquifer, reduced its volume, and became health risks for anyone drinking water from an Ogallala source.
Why do we allow such things to happen?
My personal belief is that the north and the Midwest will undergo an economic and population resurgence in the coming decades because of water. Single states with thousands of lakes can support businesses and families far more affordably than the desert Southwest. Phoenix and Los Angeles consume most of the water of the Colorado River and leave nothing more than a sand bar at the Gulf of California because the river is used up before its arrival. Arizona diverts Colorado River water into the Salt River Project canals for delivery to Phoenix, one of the hottest, driest, and fastest-growing cities in the entire world.
Why has America not devised a sustainable strategy for water use?
Questions about water in Texas and the Southwest will be a part of the purview of this newsletter in the coming months, and maybe years. The topic is far too broad to address in one edition, and the details are critical to understand, which I will pursue, even though I am a desert rat now, drawn for decades to the high, dry expanses of the American West, the long, jagged horizons, and impossible sunsets. The bright red buds of an ocotillo in spring or a blooming prickly pear will make anyone believe it is possible to thrive in an arid land. Even glorious desert flora need water, though.
We are all haunted by waters.